Visual Project Management: Everything You Need to Know
Visual project management has been creating a buzz in the project management arena, and it’s not difficult to see why. Visuals are captivating, and now that most companies have adopted a lean culture, project managers no longer have the time to go through multiple reports. Regular status briefings are also not enough to gain a complete picture of the project’s status, which is where visual task management comes into play.
It allows you to plan, execute and monitor the progress of your project quickly, without having to read multiple reports. Visuals also bring ideas to life and make complex ideas easier to understand, saving valuable time. Simply put, visual project management allows you to track your project in an easy and fun way. In this guide, we’ll highlight why you should embrace this method of task management.
What Is Visual Project Management?
Visual project management effectively plans and manages projects using tools and techniques such as calendars, Kanban boards, and timelines. These layouts allow you to visualize the progress of your project and give you quick insights into the key deliverables at a glance or in a digestible format.
Regardless of the projects you are managing, you need to find an effective way of planning and tracking the milestones. For instance, you need to know who’s responsible for what, key pieces essential to the project’s success, and any areas that are delaying project progress.
While traditional project management tools get the job done, they are ineffective. For example, spreadsheets and lists may contain all the important information, but it can take time to determine the true progress of your projects. This is because they are text-based, and let’s face it: the business environment is now so fast-paced that document-heavy processes just don’t cut it anymore.
How Do You Visualize a Project?

Research shows that your brain can process images in about 13 milliseconds, which is why visuals are an effective project management tool. They also allow you to capture and retain information easily.
IG Content:
6 Steps to Visualize a Project
- Plan your entire project schedule, including the important milestones and deadlines.
- Use a chart to organize your team while showing the relationship between all the key stakeholders.
- Present the data visually using maps, charts, infographics, and other images that allow for at-a-glance comprehension.
- Create a risk breakdown structure to assess the tentative project risks.
- Use a status report to track the project’s progress. Ensure everyone involved is updated periodically.
- Use color coding for effective communication. All project materials should be available for all stakeholders so everyone can see project progress in real time.
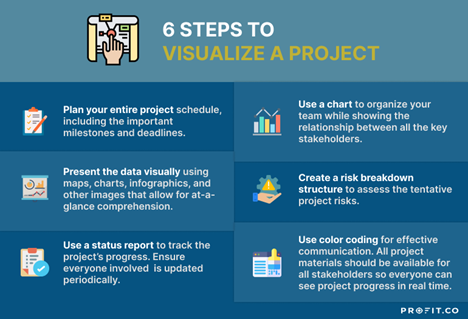
Here’s a step-by-step guide into how you can visualize your projects:
- Plan your entire project schedule, including the important milestones and deadlines.
- Use a chart to structure your team while showing the relationship between all the key stakeholders.
- Present the data visually using maps, charts, infographics, etc.
- Create a risk breakdown structure to assess the tentative project risks.
- Use a status report to track the project’s progress.
- Use color coding for effective communication.
The whole idea is to make sure that all the project’s key moving parts are organized & easy to identify and that everyone is kept in the loop.
Advertisement
[widget id=”custom_html-68″]
What Are the Benefits of Visual Task Management?
Here’s why you should adopt visual project management:
- It enhances communication across all project levels.
- It saves you time as you’re able to monitor the project’s progress at a glance.
- It gives you clarity on the entire project and makes it easy to identify roadblocks slowing you down.
- It allows you to make data-driven decisions.
Most importantly, visual task management helps you understand the true impact of making changes to a project in real-time.
What Are the Main Methods of Visual Representation of Projects?
There are 5 main tools you can use to make a visual project;
I. Calendars
Project calendars are straightforward, and they come in handy when there are multiple tasks to manage, all with varying due dates. They help you keep track of key deliverables and milestones as well as plan ahead for successful execution. You can use them on your social media calendars, editorial calendars, or other projects that require earlier preparation.
II. Kanban Boards
Kanban boards are essential for projects with distinct stages such as website development, sprint planning, bug tracking, and word results. They are visual tools that use cards to represent projects. These cards are then arranged in columns highlighting the project milestones, task priorities, and responsible personnel. When the project is completed, the cards are moved to the next stage, allowing you to identify the task progress at a glance.
III. Timelines and Charts
Project timeline or Gantt charts come in handy for projects with definite start and end dates. They help you organize your entire project schedule so that everyone involved in the task is aware of the deadlines and the time each task should take. Some of the perfect tasks for timelines and charts include product launches, campaign management, and event planning.
IV. Dashboards
Dashboards treat your project as a car and use intuitive tools such as charts and graphs to help you track the task progress. They highlight all the important project information on one page, showing you the overall progress. You can use this visual tool to check the status of tasks, track KPIs and manage the key resources. The dashboards you use should be intuitive and easy to navigate for maximum efficiency.
V. Mind Maps
We’ve all been in a situation where we know what we’d like to achieve but have a hard time organizing our ideas. Well, mind maps can come in handy during brainstorming sessions. They allow you to highlight your main ideas and then create sub-ideas below them until you have everything figured out. You can also use them when collaborating with the team to create a project plan.
Statistics reveal that around 48% of all organizational projects aren’t completed on time. This is shocking. By using the above visualization tools, you’ll be able to see the bigger picture without missing the key details.
FAQs
- What Are the Four Types of Project Management?
- Waterfall: This technique involves working on your project in waves, such that each project stage is dependent on the previous one.
- Agile: This method involves working on projects quickly, mostly by breaking them down into smaller projects that several teams can handle.
- Scrum: This technique uses sprints to complete projects.
- Lean: This project management method is all about achieving maximum project efficiency while putting the customer’s needs first.
- How Do You Visually Track a Project?
The best way to visualize a project is by first breaking it down into several phases and then creating timelines, defining KPIs, and highlighting important milestones. You should then communicate this plan to your team for maximum efficiency.
- What Are the Five Elements of Project Management?
- Conception and initiation: This is the beginning of the project, and the task details are usually broad.
- Project planning: At this stage, you should set goals and create a roadmap of how and when your project should be completed.
- Project execution: This is where you develop deliverables and complete them. You can also make modifications when needed.
- Project monitoring: At this stage, you keep track of the performance and progress of the tasks.
- Project completion.
Streamline Your Project Management Today!
There are many frameworks and methodologies you can combine with visual project management to help better streamline your achievement and success.
Combining project management with a robust performance management program, for example, can help hold your team accountable for their deliverables, as well as offer them continuous feedback so they can constantly improve their performance on a certain project. Give your team an opportunity to evaluate themselves, and show them self-evaluation examples so they know exactly what information they should share with you. This will help you gain a better understanding of how they see themselves and their contributions in the organization.




