‘Delay Thinking’ Is a Project Success Factor
Often, it is better to spend more time than it is to speed to meet a deadline. Fast is good but not always. When rushing to get something done the probability of causing damage is high.
Delay Thinking
Delay thinking recognizes that there is a delay or lag between an action and its effect. Peter Senge in The Fifth Discipline says that “Delays can make you badly overshoot your mark, or they can have a positive effect if you recognize them and work with them.”
Figure 1 below is a diagram that explains the delay phenomena, he gives the example of the delay between the time you adjust the water temperature in the shower and the time the water reaches the desired temperature. If you understand the delay, you will make sure you don’t get doused in cold water or make the mistake of further turning up the hot.
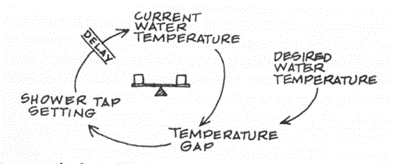
What Does This Have to Do with Projects?
In both projects and operations, we make and act upon decisions. We set expectations among stakeholders about outcomes. We are expected to fix problems and do it fast.
Faced with problems we may seek quick fixes by applying solutions that worked in the past or in other organizations. We can be pressured into rushing ahead without doing the due diligence of assessing causes, multiple scenarios, and the impact of differences between the current situation and the ones in which a solution worked in the past.
In time bound projects, there is a tendency to overlook likely delays. For example, underestimating the time it takes to perform predecessor tasks when scheduling resources. The result is the cost of resources sitting idle while waiting for the results they need to proceed.
When we take delays into consideration expectations are realistic and problem resolutions end up making things better rather than worse.
Learning Curves and Change Management
For example, when a large organization implemented a system to reduce the effort of field managers by applying AI to automate their ordering process, they failed to recognize the delay caused by a combination of learning curves, manager resistance to a perceived loss of authority and autonomy, and the need to fine-tune the algorithm used to make ordering decisions. The result was avoidable chaos, supply chain disruption, and degraded performance. The new system was rejected.
The outcome would have been a far happier one had the project plan included a robust training process, “marketing,” and a calibration period with an incremental system rollout rather than a “big bang” implementation. All of these are “delays” that on the surface cause the project to run longer. Though more often than not, when looking below the surface these so-called delays save time, effort, money and reduce unnecessary stress.
Causes
What might cause failure to include delays in plans?
Everything has a cause and when we discover causes, we can better avoid repeating failures and making poor choices.
One predominant cause of this failure to consider delays is rushing to get a project completed in a certain time frame. The pressure to get your project done by a fixed date may be driven by many things – the whim of a senior stakeholder, funding availability, the need for resources on other planned projects, legal restrictions, seasonal weather conditions, etc.
When a “get it done by” mandate is in play, pressure, and the anxiety it brings leads decision makers to cut corners, perhaps forgetting that spending more time planning can result in exponentially less time during the rest of the project. Pressure and anxiety also lead to applying quick fixes which overlook long term consequences.
Expediency bias operates even when there is no major pressure to hit a deadline. It is the tendency to prefer quick action over taking the time to make sure there is clarity and understanding about short and longer-term results.
During planning, rushing and expediency bias leads to only looking at one scenario instead of a few. Assessing multiple scenarios opens the decision to useful analysis. But this takes time. When rushing, talk about lags or delays is impatiently squelched. The risk of making a poor decision based on limited information is high.
Advertisement
[widget id=”custom_html-68″]
Quick Fixes – Short Term thinking
Another dimension of delay thinking is the recognition that when resolving a problem, while short-term fixes might remove symptoms there is a delay before the nature of longer-term consequences are experienced.
We are often blind to the long-term effects of short-term decisions and actions. When there is a lag between our action and its effect, we are easily driven by the satisfaction of short-term pleasure and immediate gratification.
Take the decision between eating a bowl of ice cream and a salad. If you are like me, the ice cream is far more pleasing than the salad. And, at the end of the day, you’d look and feel the same regardless of your choice. So why not go for the ice cream.
But factor in delay thinking and you get to see that if you repeatedly opt for the ice cream over the salad the delayed longer-term effects start to show – weight gain, digestive issues, increased blood sugar levels, etc.
Looking at the short and long-term effects makes your decision making more effective. You know what you are gaining and giving up when you make your choice. You can opt for ice cream sometimes, but you are more likely to moderate, assuming your goal is good health. You can remove symptoms with a quick fix, but you had better consider the longer term impact and plan for it.
Awareness
Awareness is the key.
Being aware that delays are normal parts of experience makes it likely that we will consider them when making decisions and planning projects. Knowledge of the specific delays in your project comes from analysis and experience, your own and your institution’s.
Be aware of rushing and expediency bias and the power of spending more time in planning to playout various scenarios, consider delays and delayed effects, and cause removal vs. symptom removal options and their effects.
Think of what happens when you drop a stone into a pond of still water. Be aware that every action you take has a ripple effect and that the ripples appear over time, radiating in all directions.




