Securing the Road Ahead: The Transformative Impact of Cybersecurity and Software Updates on the Product Lifecycle in the Automotive Industry
Abstract
A final project end with the “start of production”? No more today.
In the automotive industry, Cybersecurity and Software Updates have become critical factors that impact the entire product lifecycle. Cybersecurity and Software Updates have become a serious concern in the automotive industry with the increasing use of technology and networks in modern vehicles, as they open up new attack paths for hackers to negatively influence a vehicle’s functionality. So, how do we protect vehicle occupants from such attacks? The UN Regulations UN ECE R155 and R156 request the automotive industry to establish a Cybersecurity and Software Update Management System to enable protection throughout the whole product lifecycle against attacks from outside and avoid potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities of the system.
This calls for thinking further into the product lifecycle, as securing the vehicle must address not only the development phase, but also the production and on-road phases.
In this article, I describe how this further thinking can be established in an automotive industry organization.
The vital importance of Cybersecurity and Software Updates
Cybersecurity and Software Updates are of the highest importance in the automotive industry due to the increasing integration of advanced technologies and connectivity in modern vehicles. As cars become more connected and autonomous, they are exposed to a wide range of cyber threats, making cybersecurity a critical aspect of the whole product lifecycle.
Connected vehicles rely on a complex network of electronic control units that communicate with each other to perform various functions. If hackers gain unauthorized access to these systems, they could potentially manipulate or disable them, leading to life-threatening situations for drivers, passengers, and pedestrians.
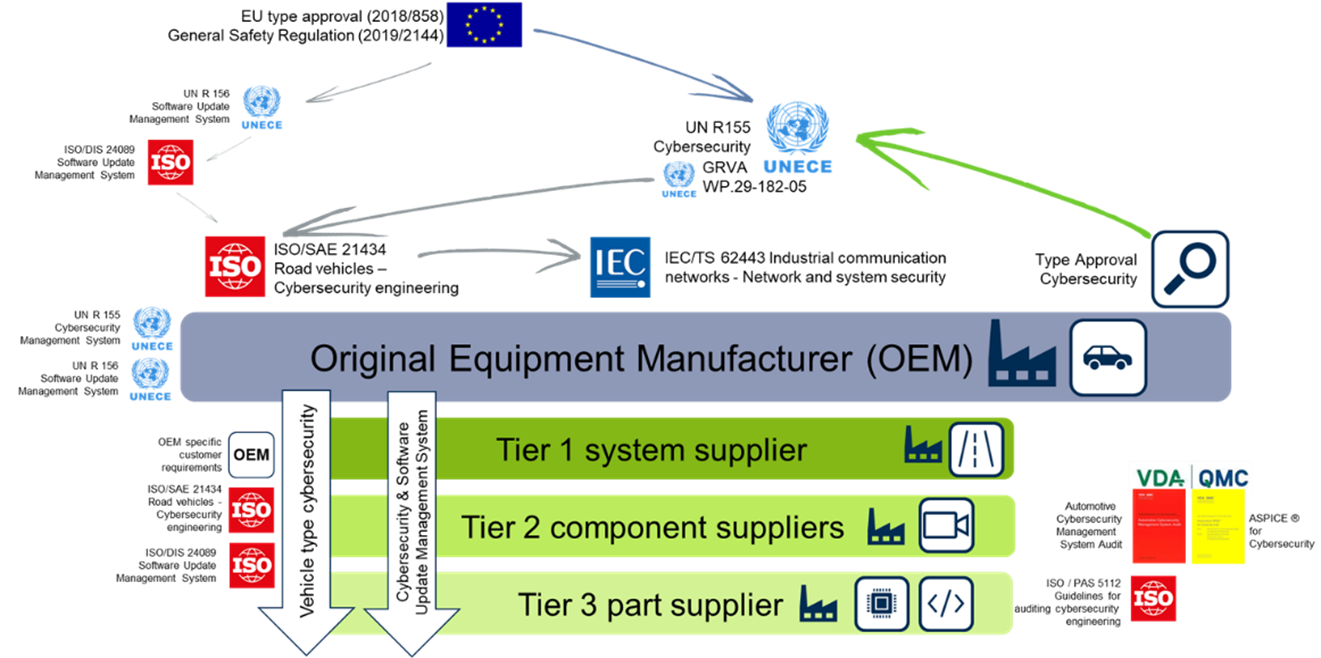
To preserve safety, security, and trust throughout the whole lifetime of the vehicles, the UN ECE Regulations require that measures are implemented across four disciplines by Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs):
- Managing vehicle cyber risks.
- Securing vehicles by design to mitigate risks along the value chain.
- Detecting and responding to security incidents across the vehicle fleet.
- Providing safe and secure Software Updates and ensuring vehicle safety is not compromised, introducing a legal basis for so-called over-the-air updates to onboard vehicle software.
The regulations apply to passenger cars, vans, trucks, and buses. They entered into force on 22nd January 2021. In the European Union, the new regulation on Cybersecurity and Software Updates will be mandatory for all new vehicle types from July 2022 and will become mandatory for all new vehicles produced from July 2024. I assume no one would drive a car if they would not trust its functionalities. To ensure Cybersecurity along the supply chain, various standards and norms are vital for the suppliers, too.
Securing the journey: How do Cybersecurity and Software Updates impact every product lifecycle stage?
Cybersecurity and Software Updates are an essential consideration during the entire product lifecycle, from conception to disposal:
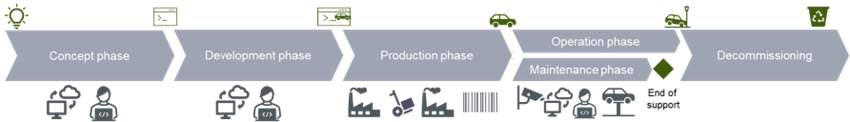
Cybersecurity and Software Update management
Is the product Cybersecurity relevant? Every project must consider this as the initial question. Effective Cybersecurity project management requires a deep understanding of cybersecurity principles and practices. By effectively managing Cybersecurity projects, organizations can enhance their security posture and mitigate cybersecurity risks. Software Updates already require thinking beyond the production phase at the very beginning. How can I secure Software Updates in the field? And most important: keep your suppliers in the loop. One small leak at the very end of the supply chain may affect the whole product.
Concept phase
The key changes of the concept phase are to identify and assess potential Cybersecurity risks and threats related to the item. This involves analyzing the item’s assets. Clear and measurable Cybersecurity Goals must be defined to guide the implementation of Cybersecurity measures.
Advertisement
[widget id=”custom_html-68″]
Development phase
In the design phase, it is essential to incorporate Cybersecurity measures and Software Updates procedures into the product’s architecture, features, and functionality. Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities throughout the development is necessary, too, to stay up to date regarding any threats to develop countermeasures to address them.
Developers must follow secure coding practices and regularly test the product for vulnerabilities. Regular screening for Cybersecurity Events that may be exploited as a weakness, vulnerability, or incident in the item is key for secure development. Those vulnerabilities are to be managed to reduce the risks of exploitation. Additionally, procedures for Software Updates campaigns and packages are already to be defined during the development, which then shall be rolled out in the field.
Before release, the product should undergo thorough testing to ensure that it meets security requirements and standards. This includes functional and security testing, including vulnerability and penetration testing. A validation shall determine if the Cybersecurity goals are achieved.
Production phase
The production of the item must be configured securely. This includes implementing secure access controls, applying security patches, and configuring firewalls and other security measures during production.
Operation and maintenance phase
Throughout the product’s lifecycle, monitoring and maintaining its security posture is essential. This includes regularly updating and patching the product, monitoring for Cybersecurity incidents and vulnerabilities, and responding to incidents promptly.
Decommissioning phase
Finally, when the product is no longer in use, it should be decommissioned of securely. Wiping data and securely destroying hardware to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information is key.
By incorporating Cybersecurity and Software Update mechanisms into each stage of the product lifecycle, organizations and their suppliers can mitigate the risk of Cybersecurity incidents and protect their customers’ sensitive information through secure Software Updates.
Who supports the setup of a Cybersecurity Management System and Software Update Management System?
Besides the UNECE Regulations for the OEMs, there are several norms, standards, and frameworks that support the setup of a Cybersecurity and Software Update Management System at the supplier’s site. As we know: we need to ensure Cybersecurity and Software Updates along the whole supply chain, these norms provide guidelines and best practices to help organizations establish effective cybersecurity measures. The two most prominent ones for Cybersecurity and Software Updates are the
- ISO/SAE 21434 „Road vehicles – Cybersecurity engineering“.
- ISO 24089 “Road vehicles — Software update engineering”.
Both norms describe the Cybersecurity and Software Update engineering processes in the automotive industry to secure the systematic development of safe vehicles – only a secure vehicle can be safe. Therefore, the norms also require security throughout the entire vehicle lifecycle. Without Cybersecurity and the associated requirements for Software Updates, there will be no sufficient Functional Safety – there is no Safety without over-the-air updates.

Securing the foundation: Transform your organization to establish a sustainable Cybersecurity Management System and Software Update Management System
Why are Cybersecurity and Software Updates so important? The answer to this question must be anchored in the mind of every colleague. Implementing a Cybersecurity and Software Update Management System requires not only the organization to define standards, rules, and processes that shall be used during the projects. It also requires the awareness of the whole staff. When you perform an organizational transformation there must always be a clear reason for the change. Get your team together, get the commitment, capture, and communicate the reasons for the change and create common sense.
Establish visionary leadership to transmit awareness to all employees and create a willingness to contribute. Create the desire and opportunities for contribution to engage the employees. Enable the staff to fulfill their roles. And anchor the new way of working and enforce the growth mindset – thrive on challenges, cultivate your qualities, and grow through application and experience.
